Komi language
Uralic language that is spoken on the Republic of Komi, Russia
The Komi language (Komi: коми кыв, komi kyv), also known as Zyryan, Zyrian or Komi-Zyryan (Komi: коми-зырян кыв, komi-zyrjan kyv),[2] is one of the two types of the Komi language. The other type is Permyak.
| Komi language | |
|---|---|
| коми кыв komi kyv | |
| Native to | Russia |
| Region | Komi Republic, Nenetsia, Permyakia, Yamalia, Yugra, elsewhere in Russia |
Native speakers | 160,000 (2010 census)[1] |
Uralic
| |
| Cyrillic,Old Permic Script (Formerly) | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | kv |
| ISO 639-3 | kpv |
| Glottolog | komi1268 |
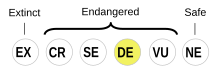 Komi is classified as Definitely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger (2010) | |
Speakers
Komi is spoken by the Komi peoples native to the Komi Republic and other parts of Russia such as Nenetsia and Yamalia. There were 285,000 speakers in 1994. This went down to 160,000 in 2010.
Writings
It was written in the Old Permic alphabet (Komi: Template:Script/Old Permic, Анбур, Anbur) in the 14th century. The Cyrillic script was introduced by Russian missionaries in the 17th century. This script replaced the Old Permic script.
References
Bibliography
- Bartens, Raija (2000). Permiläisten kielten rakenne ja kehitys (in Finnish). Helsinki: Suomalais-Ugrilainen Seura. ISBN 952-5150-55-0.
- Abondolo, Daniel (2015). The Uralic Languages. Routledge
- R. M. Batalova. 1993. Komi(-Zyryanskij) Jazyk. In V. N. Jartseva (ed.), Jazyki Mira: Ural'skie Jazyki, 214–229. Moskva: Nauka.
- Fed'un'ova, G.V. Önija komi kyv ('The Modern Komi Language'). Morfologia/Das’töma filologijasa kandidat G.V.Fed'un'ova kipod ulyn. Syktyvkar: Komi n’ebög ledzanin, 2000. 544 pp. ISBN 5-7555-0689-2.
Other websites
 Media related to Komi language at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Komi language at Wikimedia Commons

Komi edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
- Books in Komi-Zyrian from Finno-Ugric Electronic Library (by the Finno-Ugric Information Center in Syktyvkar, Komi Republic (interface in Russian and English, texts in Mari, Komi, Udmurt, Erzya and Moksha languages))
- Komi–Russian & Russian–Komi Online Dictionaries
- Tarabukin I.I. Komi–Russian Phraseological Dictionary. Archived 2011-11-23 at the Wayback Machine
- Komi Grammar. (in Russian)
- Komi-language courses
🔥 Top keywords: Main PageSpecial:SearchSupreme Court of the United StatesList of UEFA European Championship finalsWikipedia:AboutList of U.S. statesHelp:ContentsHelp:IntroductionKnights of the Round TableList of Disney moviesBlackSpecial:RecentChangesGodzilla X Kong: The New EmpireList of people who have walked on the MoonList of U.S. states and territories by time zoneUnited StatesThe Garfield MovieEducation24-hour clockEid al-AdhaGolden EdgeQueen (band)List of countries by continentsAviciiBig Mac IndexAdolf Hitler UunonaUmro Ayyar - A New BeginningMurder of Junko FurutaHelp:Authority controlCristiano RonaldoBismillahir Rahmanir Raheem19 Kids and CountingSOLID (object-oriented design)Jude BellinghamXXXTentacionLisa SparxxxPeriodic tableList of fruitsBTS
