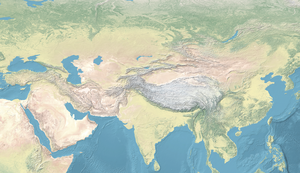
The Sauromatian culture (Russian: Савроматская культура, romanized: Savromatskaya kulʹtura) was an Iron Age culture of horse nomads in the area of the lower Volga River to the southern Ural Mountain, in southern Russia, dated to the 6th to 4th centuries BCE. Archaeologically, the Sauromatian period itself is sometimes also called the "Blumenfeld period" (6th-4th centuries BCE), and is followed by a transitional Late Sauromatian-Early Sarmatian period (4th-2nd centuries BCE), also called the "Prokhorov period".[3]
Location of the Sauromatian culture and contemporary cultures circa 500 BCE.[1] | |
| Geographical range | Southern Ural |
|---|---|
| Period | Iron Age |
| Dates | 6th-4th century BCE |
| Preceded by | Srubnaya culture Andronovo culture Cimmerian culture[2] |
| Followed by | Sarmatian culture |
The name of this culture originates from the Sauromatians (Ancient Greek: Σαυρομάται, romanized: Sauromatai; Latin: Sauromatae [sau̯ˈrɔmat̪ae̯]), an ancient Scythian people mentioned by Graeco-Roman authors, and with whom it is identified. The Sauromatian culture was nomadic: no permanent settlements have been found, and they are only known from some temporary camps and large kurgan tombs.[4]
Origins
The Sauromatian culture emerged during the 6th century BCE out of elements of the Bronze Age Srubnaya culture and the neighbouring Andronovo culture, combined with Saka nomadic elements from Central Asia.[5][6][7][8] The Sauromatian culture was first mentioned and named by Herodotus (484–c.425 BCE), who explained that it was located to the east of the Don River, 15 days distance from the northern part of the Sea of Azov.[9]
Transitional period (8th-7th centuries BCE)

The Andronovo culture and the Timber Grave culture (Srubnaya culture) seem to have merged into a transitional culture during the 8th–7th centuries BCE. Still, there are wide regional and ethnic variations: the western populations of the lower Volga River were mainly influenced by the Timber Grave culture and their anthropomorphic type was Mediterranean, while smaller populations in the Samara-Ural area were mainly influenced by the Andronovo culture and had Europoïd-Andronovo anthropomorphic types.[5]
The Sauromatian period (6th-4th century BCE) conventionally starts in the 6th century CE, after this transitional period. Throughout the period, an important influx of nomadic populations from Central Asia took place, which shaped the Sauramatian culture of the southern Ural area.[11]
The Sauromatian culture also interacted with the western Ciscaucasian group of the Scythian culture, due to which it exhibited many resemblances to this latter group of the Scythian culture.[7] From the 7th-6th century BCE, Sauromatian artistic designs started to appear in western Scythian art, which became more intricate as a result.[12]
Culturally, the Sauromatian culture was also affected by the culture of the Persian Achaemenid Empire, whose influence reached them through Central Asia. This Achaemenid influence was most prominent in the north-eastern part of Sauromatian territory during the 6th century BCE.[13] Greek influence took over from the 4th century BCE, and Greek artifacts can be found in the nomadic burials of this period, as far as the southern Urals.[14]
Location and identification
The Sauromatian culture covered an area ranging from the eastern foothills of the lower Don river in the west to the lower Volga river in the east, and from the southern Ural Mountains in the north to the eastern foothills of the Caucasus in the south.[7]
The Sauromatian culture was divided into two main local groups: a Samara-Ural group from the southern Urals to the Caspian Sea, and a Lower Volga group located between the Volga River, the Don River, and the Transvolga. The Samara-Ural group of the Sauromatian culture has not yet been identified with any population recorded by ancient authors.[6][8] Nomads of the south Uralian region are sometimes identified with the tribes mentioned by ancient authors, such as the Issedones or the Dahae.[15] As can be inferred from their closeness, close kin connections existed between the Lower Volga and the Samara-Ural groups.[6] Still, an argument has been made that they also could be considered as two different cultures.[5]
The Samara-Ural group
The region south of the Urals was very sparsely populated, "almost uninhabited", during the end of the Bronze Age, as known burials, which were of the Andronovo type, were extremely few.[5][20][11] Archaeological research suggests that the area only started to develop and population started to increase when it received waves of Asian nomadic migrations from the 7th-6th century BCE.[11][21]
From the 7th century BCE, Pamir-Ferghana anthropological types started to appear, and Eastern influence became prevalent, mainly through migrations.[5] Characteristic Saka-style deer stones are recorded in near the kurgans of Gumarovo.[22] Recent studies suggest that the population of the southern Urals actually became quite multi-ethnic, and the term "Early nomads of the southern Ural piedmont" is now often preferred to the traditional historical term "Sauromatians".[11] Early Saka nomads had started to settle in the Southern Urals as early as the 7th century BCE, coming from Central Asia, the Altai-Sayan region, and Central and Northern Kazakhstan.[23] The Itkul culture (7th-5th century BCE) is one of these Early Saka cultures, based in the eastern foothills of the Urals and specialized in metallurgy, which was assimilited into the Early Sarmatian culture.[23] Circa 600 BCE, groups from the Saka Tasmola culture settled in the southern Urals.[23] Circa 500 BCE, other groups from the area of Ancient Khorezm settled in the western part of the southern Urals, who also assimilated into the Early Sarmatians.[23] All these nomadic populations are identified by their kurgan burial mounds and their numerous artifacts, such as Taksai kurgans (c.500 BCE).[11] Other south Ural kurgans of the 6th-4th centuries BCE include the kurgans of Kyryk-Oba, Lebedevka, Tara-Butak, Akoba, Nagornoye, Zhalgyzoba etc...[24]
Late Sauromatian-Early Sarmatian period
As a result, a large-scale integrated union of nomads from Central Asia formed in the area in the 5th–4th century BCE, with fairly uniformized cultural practices.[23] This cultural complex, with notable ‘‘foreign elements’’, corresponds to the ‘‘royal’’ burials of the Filippovka kurgans (c. 400 BCE), and defines the "Early Prokhorovka period" of the Late Sauromatian-Early Sarmatians.[23] The Sauromatians of the southern Ural, such as those buried in the Filippovka kurgan (c.400 BCE), combined Western (Timber Grave and Andronovo) and Eastern characteristics, and generally displayed an increased incidence of eastern Asiatic features.[25] They most closely resembled the Saka populations of Central Asia, particularly from the Altai region (Pazyryk), and were very different from the western Scythians, or even the Sarmatians of the Volga River area to the west.[25] The archaic stle of the animal style in the Filippovka kurgan prompted some authors to date it to the 6th century BCE.[26]
The culture of the Samara-Ural group ended in the first decades of the 3rd century BCE (circa 300-250 BCE), possibly due to changing climatic conditions and the arrival of new nomads from Central Asia and southern Western Siberia, possibly Alans, which defined the succeeding Sarmatian period.[23] Sarmatian culture is generally thought to have formed in the Ural steppes, and the general westward mouvement of these nomadic tribes may have provoked the demise of the classical Volga Sauromatians, who may even have belonged to a different genetic profile.[27][28]
- Two-planed stag, Filippovka kurgan, Late Sauromatian-Early Sarmatian, 4th century BCE.[29]
- Amphora with argali-shaped handles, Filippovka kurgan 1, 4th century BCE.
- Gold bear, Filippovka kurgans, Late Sauromatian-Early Sarmatian, 5th-4th century BCE.[30]
- Warriors with daggers and bows. Dagger blade decoration from Kurgan 4, Burial 2, Filippovka, Late Sauromatian-Early Sarmatian, 5th-4th century BCE.[31]
The Lower Volga group
The section of the Lower Volga group of the Sauromatian culture located between the Don and Volga rivers corresponds to the Sauromatians mentioned by Graeco-Roman authors.[6][8] They first formed during the 7th century BCE, after the Scythians had migrated westwards and become the masters of the Pontic–Caspian steppe. The historian Marek Jan Olbrycht has suggested that the Sauromatians might have been a Scythian group who migrated from Media during the period of Scythian presence in Western Asia, after which they merged with Maeotians who had a matriarchal culture. These early Sauromatians lived in the area of the Don river, near the Sea of Azov in the North Caucasus,[8] and their western neighbours were the Scythians proper.[7]
The Sauromatians may have been the Saⁱrima- (𐬯𐬀𐬌𐬭𐬌𐬨𐬀) people mentioned in the Yašts as one of the five peoples following the Zoroastrian religion, along with the Aⁱriia- (𐬀𐬌𐬭𐬌𐬌𐬀), Tūⁱriia- (𐬙𐬏𐬌𐬭𐬌𐬌𐬀), 𐬛𐬁𐬵𐬀 (Dāha-), and Sāinu- (𐬯𐬁𐬌𐬥𐬎), although this identification is still uncertain.[8][32]
Social and economic development


The burials of the Lower Volga Sauromatians were poorer and less sophisticated than those of their neighbours, either those of the Scythians to the southwest or the southern Urals Sauromatians to the northeast. This suggests that Lower Volga Sauromatians had a lesser level of social and property differentiation. The kurgans of the southern Urals Sauromatians were much larger and richer, suggesting the existence of a rich military aristocracy in the 5th century BCE. No such burials have been found in the Volga area, suggesting that a more basic clan structure remained in place, with a poorer and weaker military aristocracy.[35]
Political development
According to the Greek historian Herodotus, the Sauromatians were descendants of Amazons and young Scythians who lived in the area beyond the Tanais. Women rode on horseback, joined their husbands in war, and wore the same dress as men.[36] The Sauromatians spoke a "corrupt form" of the Scythian language, which might be explained by the influence of the Andronovo culture in the development of the Sauromatian culture.[6]
During the 6th to 5th centuries BCE, the Lower Volga Sauromatians were constituted of either a number of tribes or of a single tribe sharing a common ethnic identity, and united into a single polity bounded to the west by the Don river and to the east by the Volga river. By the end of the 5th century BCE, groups of the Sauromatians had moved to the west and settled around Lake Maeotis along the Royal Scythians and the Maeotians.[6][8][37]
The Sauromatians maintained peaceful relations with their western neighbours, the Scythians, who were also an Iranic equestrian nomadic people. A long road starting in Scythia and continuing towards the eastern regions of Asia existed thanks to these friendly relations.[6]
When the Persian Achaemenid king Darius I attacked the Scythians in 513 BCE, the Sauromatian king Scopasis supported the Scythians.[6]
During the 6th century BCE, related Iranic nomads from the Central Asian steppes migrated westwards into the country of the Lower Volga Sauromatians, due to which the bulk of the Sauromatians retreated to the west, in western Ciscaucasia.[38] Due to this, the Scythians progressively lost their territories in the Kuban region to the Sauromatians over the late 6th century BCE, beginning with the territory to the east of the Laba river, and then the whole Kuban territory.[39]
By the end of the 6th century BCE, the Scythians had lost their territories in the Kuban Steppe and had been forced to retreat into the Pontic Steppe, except for the westernmost part of the Kuban Steppe, which included the Taman peninsula,[40] where the Scythian Sindi tribe formed a ruling class over the native Maeotians, due to which this country was named Sindica. By the 5th century BCE, Sindica was the only place in the Caucasus where the Scythian culture survived.[39][41]
The retreating Sauromatians continued to move westwards, migrating into Scythia itself[42] over the course of 550 and 500 BCE and were absorbed by the Pontic Scythians with whom they mingled. A large number of settlements in the valleys of the steppe rivers were destroyed as a result of these various migratory movements.[40][41]
The retreat of the Scythians from the Kuban Steppe and the arrival of the Sauromatian immigrants into the Pontic steppe over the course of the late 6th to early 5th centuries BCE caused significant material changes in the Scythian culture soon after the Persian campaign which are not attributable to a normal evolution of it. Some of the changes were derived from the Sauromatian culture of the Volga steppe, while others originated among the Kuban Scythians, thus resulting in the sudden appearance within the lower Dnipro region of a fully formed Scythian culture with no local forerunners, and which included a notable increase in the number of Scythian funerary monuments.[43][41]
Characteristics

Sites belonging to the Sauromatian culture consist of kurgans whose contents are poorer than those of Scythian burials, attesting of the presence of less extensive class stratification among the Sauromatians as compared to their western Scythian neighbours.[6]

The remains of the Sauromatian culture consist nearly only of graves, which were themselves mostly secondary burials that had reused older kurgans. The grave goods present in these burials characterised the Sauromatians as well-armed cavalry warriors, although many of them appear to have also fought on foot.[7]
The Sauromatian kurgans of the 5th century BCE found in the southern foothills of the Ural Mountains were, however, more developed, large and rich, and belonged to a military aristocracy. One example of such rich Sauromatian sites is the Pyatimary (Пятимары) group, located on the Ilek river.[6]
The Sauromatian kurgans of the Volga area were instead all poorer, and none of them possessed the stature and richness of the Ural kurgans. This is an attestation of the clan structure of Sauromatian society subsisting for longer in the region between the Don and the Volga, while the tribal aristocracy in this area was weaker in both economic and military terms as compared to the aristocracy near the Urals.[6]
The presence of pedestalled sacrificial altars made of stone or flat stone dishes with raised rims in female Sarmatian graves also confirms that claims of Graeco-Roman authors that Sarmatian women were warriors as well as priestesses. These priestesses held a very important status in Sauromatian society.[6][42]
Weapons
Numerous weapons, armour, helmets were already found in the excavations of the Early Sarmatian Filippovka kurgan (c. 450-300 BCE):[47] The weapons are very similar to those of the Tagar culture.[48]
Out of all military Sauromatian burials which contain weapons, twenty percent of the graves belong to women warriors, with this relatively large number attesting of the veracity of Graeco-Roman authors' claims that Sauromatian women held a special role and participated in military operations and in social life. Women's burials occupied the central position and were the richest in multiple Sauromatian funerary complexes.[6][42]
- Filippovka 1 Iron armour from burial 2 mound 4
- Filippovka 1, Horn armour from mound 29
- Filippovka 1, bronze arrowheads from burial 2, mound 4
- Filippovka 1, iron helmets from mound 11
- Filippovka 1, iron swords and daggers
- Filippovka 1, bronze and inlaid gold dagger

Demise


The Sauromatian culture came to an end when, in the 4th to 3rd centuries BCE, they were conquered by nomadic Central Asian populations from regions east of the Urals who moved into the trans-Ural steppes and the lower Volga region.[6][8] The Sauromatians joined these new conquerors. Their combination with these eastern nomads gave rise to the Sarmatians.[52] They were initially able to preserve their separate identity, although their name, modified into "Sarmatians" eventually came to be applied to the whole of the new people formed out of these migrations, whose constituent tribes were the Aorsi, Roxolani, Alans, and the Iazyges.[6][8][37]
Despite the Sarmatians having a similar name to the Sauromatians, ancient authors distinguished between the two, and Sarmatian culture did not directly develop from the Sauromatian culture; the core of the Sarmatians was instead composed of the newly arrived migrants from the southern Ural foothills.[6][8][37] This evolution is also reflected in the genetic profile of the Sauromatians and Sarmatians, which sees a marked influx of Central Asian nomads (Altaian-like ancestry), continuing into the Late Sarmatian period.[50]
From an archaeological standpoint, there is no continuity between the lower Volga Sauromatians and the Sarmatians of the 3rd century BCE onward. The Sarmatians were instead derived from the southern Urals Sauromatians, combined with new migrants from beyond the Urals, who migrated into the lower Volga region and conquered the lower Volga Sauromatians. Sarmatians polities such as the Aorsi, the Roxolani, the Alans and the Iazyges then became known. These powerful tribes further expanded westward and conquered the Scythians. and the north Caucasus.[53]
See also
- Savelev, Nikita S. (2021). "SMALL GUMAROVO KURGANS OF SCYTHIAN-SARMATIAN TIME AT SOUTH URAL: CHRONOLOGY, FEATURES OF THE FUNERAL RITES AND ISSUES OF CULTURAL ATTRIBUTION (CC BY)". Nizhnevolzhskiy Arheologicheskiy Vestnik. doi:10.15688/nav.jvolsu.2021.1.
References
Bibliography
- Batty, Roger (2007). Rome and the Nomads: The Pontic-Danubian Realm in Antiquity. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-198-14936-1.
- Ivantchik, Askold (2018). "Scythians". Encyclopædia Iranica. New York City, United States: Encyclopædia Iranica Foundation; Brill Publishers. Retrieved 8 August 2022.
- Melyukova, A. I. (1990). Sinor, Denis (ed.). The Cambridge History of Early Inner Asia. Vol. 1. Translated by Crookenden, Julia. Cambridge, United Kingdom; New York City, United States: Cambridge University Press. pp. 97–117. ISBN 978-0-521-24304-9.
- Olbrycht, Marek Jan (2000). "Remarks on the Presence of Iranian Peoples in Europe and Their Asiatic Relations". Collectanea Celto-Asiatica Cracoviensia. Kraków: Księgarnia Akademicka. pp. 105–107. ISBN 978-8-371-88337-8.
- Sulimirski, T. (1985). "The Scyths". In Gershevitch, I. (ed.). The Median and Achaemenian Periods. The Cambridge History of Iran. Vol. 2. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. pp. 149–199. ISBN 978-1-139-05493-5.
- Sulimirski, Tadeusz; Taylor, T. F. (1991). "The Scythians". In Boardman, John; Edwards, I. E. S.; Hammond, N. G. L.; Sollberger, E.; Walker, C. B. F. (eds.). The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries B.C. The Cambridge Ancient History. Vol. 3. Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. pp. 547–590. ISBN 978-1-139-05429-4.
- Summerer, Lâtife (1 January 2020). "The wooden comb of the 'golden lady': a new battle image from the Taksai-1 kurgan (western Kazakhstan)". Masters of the Steppe: the Impact of the Scythians and Later Nomad Societies of Eurasia. Archaeopress. pp. 588–760.
- Vogelsang, Willem (1993). "Dahae". Encyclopædia Iranica. New York City, United States: Encyclopædia Iranica Foundation; Brill Publishers.