The Rojava–Islamist conflict, a major theater in the Syrian civil war, started after fighting erupted between the Kurdish People's Protection Units (YPG) and Islamist rebel factions in the city of Ras al-Ayn. Kurdish forces launched a campaign in an attempt to take control of the Islamist-controlled areas in the governorate of al-Hasakah and some parts of Raqqa and Aleppo governorates after al-Qaeda in Syria used those areas to attack the YPG. The Kurdish groups and their allies' goal was also to capture Kurdish areas from the Arab Islamist rebels and strengthen the autonomy of the region of Rojava.[66] The Syrian Democratic Forces would go on to take substantial territory from Islamist groups, in particular the Islamic State (IS), provoking Turkish involvement in the Syrian Civil War.
| Rojava–Islamist conflict | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Rojava conflict of the Syrian civil war | ||||||||
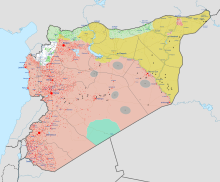 Territories held by the SDF (yellow), IS (black), the SAA (red), the Syrian National Army and Turkey (light green), Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (white), and the Revolutionary Commando Army (teal) as of November 2023 | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Belligerents | ||||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | ||||||||
(Jabhat al-Akrad general commander) | Unknown | |||||||
| Units involved | ||||||||
| IS Military | Unknown | ||||||
| Strength | ||||||||
YPG: 65,000[48] | IS: Over 15,140[52][53][54] | al-Nusra Front: 5,000–6,000[55] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | ||||||||
| 11,000 fighters killed 21,000 fighters wounded[56] | By YPG/SDF: 25,336 killed, 2,127 captured (YPG claim; 2013–2017 total)[57][58][59][60][61] By US-led airstrikes: 9,145+ killed (SOHR claim, minimum, as of March 2019)[62] | Unknown | ||||||
| Dozens of Syrian and 4 Turkish[63][64] civilians killed and 100,000[65] Syrian Kurds fleeing to Turkey | ||||||||
Background
Since the end of the Battle of Ras al-Ayn, the city was divided between an Arab-controlled western part and a Kurdish-controlled eastern part.[67] On 16 July, members of the al-Nusra Front attacked a Women's Protection Units (YPJ) patrol. They detained the driver; two female fighters managed to escape. In response to this attack, the People's Protection Units (YPG) brought reinforcements from al-Derbasiya while al-Nusra had sent 200 fighters as reinforcements a few days before.[68]
Conflict
2013
On 28 January, Arab tribesmen attacked the homes of Christian Armenians and Assyrians in the village of ad-Dalawiyah (25 kilometres (16 mi) south of Qamishli) and attempted to steal their harvest. The Assyrian Democratic Organization condemned the attacks, characterising them as "foreign deeds". Islamist rebels repeatedly called for Christians in the province to leave.[69]
Kurdish capture of Ras al-Ayn and spread of fighting
On 16 July, the Kana'is street (where the YPG was positioned) and the al-Mahatta neighborhood (where al-Nusra was positioned) witnessed clashes.[68] A few hours later, the YPG took control of the headquarters of al-Nusra and released the fighter al-Nusra had kidnapped.[70]
On 17 July, Kurdish fighters expelled the jihadists from the town of Ras al-Ayn after a night of fighting[71] and soon after took control of the border crossing with Turkey.[72] Islamist forces retreated from Ras al-Ayn to Tal Half, Asfar and Najar which were under rebel control.[73] Eleven people were killed during the fighting, including nine jihadist and two Kurdish fighters.[74]
On 19 July, the YPG captured the village of Tal A'lo.[75] Fighting was still continuing in Karhouk and A'li Agha.[76] The next day, Kurdish fighters captured an al-Nusra checkpoint near the contested villages. By this point, 35 jihadist and 19 YPG fighters had been killed in the fighting.[77]
By the end of July 2013, IS and al-Nusra expelled Jabhat al-Akrad and the YPG from the border town of Tell Abyad after a week of fighting which displaced thousands of Kurdish civilians.[78]
August–September fighting and Kurdish advances
On 1 August, IS declared the start of the siege of Kobanî, or Ayn al-Arab where the headquarters of the YPG is located. The area surrounding Kobani was then blocked on all sides by IS and the Turks.[79]
By August 28, Islamists and Kurdish forces were battling for control of the town of Yarubiya on the Iraq–Syria border. Islamists had captured further territory from the Kurds in Aleppo and Raqqa provinces; while in Aleppo, Islamists were ethnically cleansing Kurds from towns in the countryside and massacring them, leading to a mass migration of civilians to the town of Afrin.[80]
On 17 September, in the Al-Hasakah Governorate, Fighting broke out between Kurdish fighters and Islamist fighters in A'louk village that lies east of Ras al-A'in while fighting still took place near the town of al-Ya'rubiya. On 18 September, YPG took control of A'louk after four days of fighting that killed 20 people.[81]
On 26 September, rebels from the Free Syrian Army and Trotskyists of the Leon Sedov Brigade[82] joined IS in clashes with YPG forces around the town of Atma, on the Turkish border. FSA units were said to have brought heavy artillery to the battle to push back Kurdish snipers while Kurdish tanks were firing at Atma. Arab rebel artillery was launched at the town of Jindires.[83]
On 29 September, multiple bombers attacked Erbil, the capital of Iraqi Kurdistan. Six people were killed and more than 40 were injured. The IS later claimed responsibility and stated the attacks were retaliation for Masoud Barzani's stated intention of intervening in Syria on behalf of the Syrian Kurds.[84]
October Kurdish offensive
On 26 October the YPG took control of the al-Yaarubiyah border crossing with Iraq[85] as well as the town itself.[86]
On 28 October, IS front in the oil-rich Çil Axa region completely collapsed. The YPG captured the villages of Girhok, Yusufiyê, Sefa, Cinêdiyê, Girê Fatê, Ebû Hecer and Mezraa Kelem while remnants of IS forces fled to Tal Hamis and Tal Brak.[87]
November Kurdish offensive
On 2 November, Kurdish forces launched an offensive called the "Serekeniye Martyrs' Offensive", with the aim of consolidating their control of Hasaka province by pushing jihadist forces out of the area surrounding Ras al-Ayn.[88]
On 6 November, in Hasakah province, the YPG took over two villages west of Tall Tamer, on the highway to Aleppo, after clashes with IS, Jabhat Al-Nusra and allied rebel groups. The towns the YPG had taken over were Ghebesh and Tal Shemarin, which are inhabited by Assyrians.[89] By this point, YPG forces had captured a total of 40 towns and villages in the offensive.[90]
On 13 November, following major gains by the YPG, the PYD announced plans to create an autonomous transitional government to run the Kurdish-majority northeast of Syria. The plans were announced after a meeting in Qamishli that also involved Christian and Arab groups. The plan called for the creation of a parliament of 82 members elected from three cantons across the region. Kurdish officials also stated that the region would continue to be managed autonomously regardless of events elsewhere. In Raqqa province, rebel fighters launched domestically manufactured rockets on the villages of Kandar and Abdi Kawi which were under the control of the YPG.[91]
On 28 November, in Al-Hasakah province, YPG fighters took of three villages (Rokoba, A'wja, and Tal Maghas) which lie on the Tal Tamer-Hasaka road after violent clashes with IS, al-Nusra and several rebel battalions.[92]
December Kurdish offensive
During the night of 26/27 December, the YPG launched an offensive on jihadist-controlled areas between Hasakah and Qamishli, during which they took Tell Brak District.
On 1 January 2014, the YPG battled the Islamists in Tell Brak, but were not able to capture the town. The battle caused 39 YPG and 21 Islamist fatalities.[93]
2014
January–February Islamist offensive and Kurdish counter-offensive
On 24 January, jihadist forces attacked the YPG-held town of Manajeer in the Al-Hasakah Governorate. However, after four days of fighting, their attack was repelled. Twenty-three Islamist and three Kurdish fighters were killed. During the fighting, the YPG also captured at least one tank from the jihadists.[94]
On 1 February, it was reported that the YPG launched an offensive against IS bases in Tell Abyad.[95]
On 3 February, the YPG claimed to have killed 8 IS fighters, including a commander, during clashes in Girê Spî.[96]
On 15 February, the YPG (supported by the Shammar tribe) launched an offensive against IS in the Tell Hamis area. Two days later, the YPG claimed to have killed "many" IS fighters and captured 30 of them, in addition to capturing five military vehicles and a large amount of weaponry during the operation.[97]
On 23 February, a predawn raid by the YPG captured Tell Brak, which lies in a strategic position between Al-Hasakah and Qamishli.[93]
On 26 February, the YPG announced it had halted all its military operations in the Kurdish-controlled regions but warned its enemies that it would respond to every hostile action on Kurdish soil.[98] The next day, IS launched an attack on Til Merûf which was eventually repelled by the YPG. According to the YPG, 16 IS fighters were killed in the clashes.[99]
March–April fighting at Tell Abyad and Kobanê
On 1 March, IS attacked villages around Tell Abyad but the attack was repelled and left one IS fighter killed, according to the YPG.[100] On 6 March, the YPG claimed to have killed 16 IS fighters and destroyed a "military vehicle" in Tell Abyad.[101]
On 11 March, IS captured the town of Sîrîn[102] and attacked the Al-Hadaya Hotel in the city of Qamishli with suicide bombs, killing nine Kurdish civilians.[103] SOHR also reported that IS executed 25 Kurds (including 14 fighters) in the Al-Sheyokh area, near Jarabulus.[104] On 13 March, IS (according to local sources) captured the Qereqozak Bridge and some strategic areas near the Tomb of Suleyman Shah in Kobanê after clashes with Kurdish fighters.[105] On 14 March, Kurdish sources claimed that the YPG and allied forces killed 35 IS fighters in clashes in the countryside of southern Kobanî Canton, which erupted after IS launched an unsuccessful attack towards the Serriin silos.[106]
On 17 March, heavy clashes erupted between the YPG and IS near the Qereqozak Bridge in Kobanê. The YPG claimed to have killed 40 IS fighters.[107] On 19 March, the YPG captured Tell Henzir village.[108] The next day, the YPG also took control of Tell Henzir, Tell Xezal Miço, Ferisa Şerabiyan, Ferisa Sofiyan, Ferisa Dişo, Tell Boğan and Tell Meha. It was also stated that 32 IS fighters were killed in the clashes.[109]
On 22 March, SOHR reported heavy clashes between IS and the YPG around many villages in the western countryside of Tell Abyad, which resulted in the fleeing of mainly Kurdish refugees from the western countryside of Tell Abyad and surrounding areas to Turkey.[104]
On 1 April, IS laid siege to Kobanê from three flanks, and launched an artillery attack from Zor Mughar. The YPG ambushed IS forces at Kendal, east of Kobanê, killing 12 Azeri IS fighters and their Kurdish commander.[110] Fighting raged in Zor Mughar and Kharab Atto while YPG fighters cut off all the roads leading to Kobanê from the western side, starting from the villages of Ta'lk, Derbazin and al-Qanaya, to prevent potential attacks by IS fighters against the city.[111] Despite YPG control of the hills around Sirrin, IS forces, backed up by tanks, captured two grain silos and seized the village of Tal al-Bawgha.[110]
The YPG, the Euphrates Islamic Liberation Front, Liwa Ahrar Souriya and the Liwa Thuwwar al-Raqqa worked together against IS in Kobanê.[112] The YPG also co-operated with the Farouq Brigades and the Liwa Thuwwar al-Raqqa in Raqqa Governorate in operations against IS.[112]
May kidnappings
On 29 May, it was reported that IS killed dozens of civilians in raids on several villages in the Ras al-Ayn region of Al-Hasakah province, with the retrieval of at least 15 bodies, including seven children.[113]
On 30 May, IS kidnapped 193 Kurdish civilians between the ages of 17 and 70 from the village of Qabasin near al-Bab. On the same day, they seized up to 186 Kurdish students who had been traveling from the Kobani region to Aleppo to complete exams.[114] The teenagers were reportedly sent to religious schools in Minjeb where they were subjected to Salafist indoctrination.[115]
July Kobanî offensive
On 4 July, using weapons captured in Iraq, IS seized the villages of Zor Maghar, Al-Zyara, and Bayadiyah, near the city of Kobanî, after three days of fighting with YPG forces.[116]
On 9 July, IS advanced towards Kobanî from the east, forcing the YPG to withdraw from the villages of Abdi, Kwi, Kendal, Kri and Sor.[117] The clashes led to the deaths of 18 Kurdish fighters.[118]
On 14 July, the PYD issued a regional call to arms for all Kurds to assist in defending Kobanî. Kurdish militants from the PKK crossed from Turkey to reinforce YPG defensive positions. By this time, at least 10 villages had fallen to IS, who had begun to lob mortars at Kobanî. At least two PKK fighters were killed while defending the canton.[119]
By the end of July, according to the PYD, IS offensive against Kobanî had been repelled, with 685 IS fighters being killed.[120]
September Kobanî offensive


On 17 September, following the capture of a strategic bridge over the Euphrates,[121] IS launched a large offensive using tanks, rockets and artillery in the direction of Kobanî, and within 24 hours captured 21 Kurdish villages. The advance left Kobanî encircled by IS forces.[122]
On 19 September, IS captured 39 more villages,[123] bringing their forces within 20 kilometers of Kobanî.[124] Forty-five thousand refugees crossed into Turkey, fearing the region would become part of IS,[125] while a number of refugees were stopped at the border and ordered to return to Kobanî by Turkish authorities.[126]
By 21 September, IS captured 64 villages[127] as their forces came within 10 kilometers of the city, and continued to advance[128] with fighting concentrated on the southern and eastern suburbs of Kobanî, 13 kilometers from the town.[129]
On 28 September, after violent clashes with the Kurdish forces of the YPG, IS militants captured the villages of Kenana, Qadaa, and Hamadaneh in the Tel Kocher (Yarubiyah) countryside.[130]
Merger with Iraqi campaign
Iraqi Kurdish Peshmerga fighters, with the aid of troops from the Syria-based Kurdish Democratic Union Party (PYD), took control of the Rabia border crossing between the two countries,[131] marking the first major battle to straddle both. On 31 October, Iraq-based Peshmerga troops crossed into Syria via Turkey to aid in the defense of the border city of Kobane.[132]
2015
January–December

The war dragged on, as both IS and the YPG gained and lost territory to each other, other rebel groups and loyalists. YPG successes alarmed the Turks, who threatened invasion.[133] In June, militants attacked Kobanî, killing over 200 people in gun battles.
Nusra-YPG clashes
On 31 July 2015, clashes erupted between YPG and al-Nusra forces in the south of the Efrin Canton, targeting the town of Cindires.[134]
On 26 September 2015, clashes erupted between YPG and al-Nusra forces in the YPG-held district of Sheikh Maqsood. The clashes resulted in YPG forces advancing and capturing Castello Road, a key rebel supply line in the rebel-held Eastern Areas of Aleppo city. Tensions continued after the YPG allegedly violated clauses of a truce with the rebels concerning Castello Road. On 1 October Nusra forces again attacked YPG positions in Sheikh Maqsood; however this was repelled, with the YPG remaining in control of the key rebel supply route.[135][136][137]
Clashes between YPG-Al Nusra were renewed in the vicinity of Sheikh Maqsood on 3 October, with Al Nusra suffering 15 casualties.[138]

Al-Hawl offensive

During November 2015, the YPG and its allies in the Syrian Democratic Forces captured the town of al-Hawl, along with more than 200 villages and towns from IS in the surrounding areas in Al-Hasakah Governorate near the border with Iraq in the month-long offensive.
Tishrin Dam offensive
In the week-long offensive, the SDF captured Tishrin Dam and surrounding villages from IS.
2016
Northern Aleppo offensive
During February 2016, Syrian government forces and allied militias, backed by Russian and Syrian airstrikes, launched an offensive to capture areas in Northern Aleppo. The YPG-led SDF followed their advances and captured the city of Tell Rifaat and the Menagh Military Airbase.
Al-Shaddadi offensive
On 16 February 2016, the SDF, supported by airstrikes from the US-led coalition, launched an offensive to capture the strategic city of al-Shaddadi from IS.
Manbij offensive

On 31 May 2016, the SDF, supported by airstrikes from the US-led coalition, launched an offensive to capture the strategic city of Manbij from IS.
Afrin Canton
On 11 September 2016 Jabhat Fateh al-Sham, the renamed al-Nusra Front, fired over 20 mortar shells at the town of Jindires in the southwestern Afrin Canton, destroying several residential buildings and causing a number of casualties, mostly women and children.[139]
Raqqa offensive
Turkish intervention (2015-present)

During the summer of 2015, Turkey began bombing YPG and PKK positions in Syria and Iraq.[140]
On 13 February 2016, Turkey began shelling the Kurdish-held areas in northern Syria.[141]
