Piceol is a phenolic compound found in the needles and in mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces (Picea abies).[1][2] Picein is the glucoside of piceol.[3]
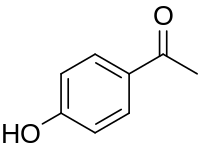 Chemical structure of piceol | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethan-1-one | |
| Other names 1-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethanone 4-Hydroxyacetophenone 4'-Hydroxyacetophenone p-Hydroxyacetophenone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.548 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O2 | |
| Molar mass | 136.150 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Uses
Piceol is used in the synthesis of several pharmaceutical drugs including octopamine, sotalol, bamethan, and dyclonine.[citation needed]
Piceol can be used to make acetaminophen by condensation with hydroxylamine and subsequent Beckmann rearrangement in acid.[4]
Anticonvulsants are also possible by Mannich reaction:[5]
Metabolism
Diprenylated derivatives of piceol can be isolated from Ophryosporus macrodon.[6]
4-Hydroxyacetophenone monooxygenase is an enzyme that transforms piceol into O-acetylhydroquinone. This enzyme is found in Pseudomonas fluorescens.
See also
- Paroxypropione, where the acetyl group is replaced by a propionyl group.
- Apocynin
References
🔥 Top keywords: Main PageShannen DohertySpecial:SearchCarlos AlcarazList of United States presidential assassination attempts and plotsAttempted assassination of Donald TrumpDonald TrumpRichard Simmons2024 shooting at a Donald Trump rallyLamine YamalNovak DjokovicNico WilliamsUEFA European ChampionshipWikipedia:Featured picturesThomas Matthew CrooksProject 2025Attempted assassination of Ronald ReaganUEFA Euro 2024Jacoby JonesAR-15–style rifleMukesh AmbaniLonglegsSpain national football teamKimberly CheatleKalki 2898 ADList of Wimbledon gentlemen's singles championsCole PalmerGareth SouthgateJohn Hinckley Jr.Harry KaneLuke PerryAntifa (United States)United States Secret Service.xxxDeaths in 2024Ruth WestheimerEvan VucciButler, PennsylvaniaIndian 2