Pi Cassiopeiae, Latinized from π Cassiopeiae, is a close binary star[8] system in the constellation Cassiopeia. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +4.949.[2] Based upon an annual parallax shift of 18.63 mas as seen from Earth,[1] this system is located about 175 light years from the Sun.
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Cassiopeia |
| Right ascension | 00h 43m 28.07045s[1] |
| Declination | +47° 01′ 28.3694″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +4.949[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A5V[3] + A5V[4] |
| B−V color index | +0.171[2] |
| Variable type | Ellipsoidal[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +12.9±0.8[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −23.71±0.23[1] mas/yr Dec.: −36.84±0.18[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 18.63 ± 0.32 mas[1] |
| Distance | 175 ± 3 ly (53.7 ± 0.9 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +1.30[7] |
| Orbit[8] | |
| Period (P) | 1.9642 d |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.00 |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2427535.74 JD |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 0.00° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 120.5 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 122.1 km/s |
| Details | |
| A | |
| Mass | 1.82[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.9[4] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 22[10] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.41[11] cgs |
| Temperature | 8,392±285[11] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 60[4] km/s |
| Age | 251[11] Myr |
| B | |
| Mass | 1.87[9] M☉ |
| Radius | 1.9[4] R☉ |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 65[4] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
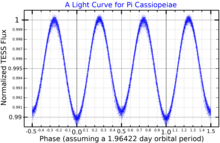
This is a double-lined spectroscopic binary system with an orbital period of nearly two days in a circular orbit.[8] It is classified as a rotating ellipsoidal variable star and its brightness varies by 0.02 magnitudes with a period of 23.57 hours,[5] which equals half of its orbital period. The spectrum matches that of an A-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of A5 V.[3] The two stars have similar masses and spectra.[4] A star at a projected separation of 1,700 AU has been identified as a possible white dwarf. It is at the same distance as Pi Cassiopeiae and shares a common proper motion. The age of the white dwarf is calculated to be about 500 million years.[14]
Pi Cassiopeiae has been given the spectral class of kA3hF1mA5, indicating an Am star,[15] but this is now considered doubtful.[16]
