Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) is a pentose phosphate. It is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, as well as in pyrimidine nucleotide formation. Hence it is a building block for DNA and RNA.[1][2][3] The vitamins thiamine[4] and cobalamin,[5] and the amino acid tryptophan also contain fragments derived from PRPP.[6] It is formed from ribose 5-phosphate (R5P) by the enzyme ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase:[7]
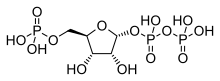 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name α-D-Ribofuranose 1′-(trihydrogen diphosphate) 5′-(dihydrogen phosphate) | |
| Systematic IUPAC name (2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-Dihydroxy-5-[(phosphonooxy)methyl]oxolan-2-yl trihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Other names 5-phospho-α-D-ribose 1-diphosphate PRPP | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| MeSH | Phosphoribosyl+pyrophosphate |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H13O14P3 | |
| Molar mass | 390.07 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
It plays a role in transferring phospho-ribose groups in several reactions, some of which are salvage pathways:[8]
In de novo generation of purines, the enzyme amidophosphoribosyltransferase acts upon PRPP to create phosphoribosylamine.[2] The histidine biosynthesis pathway involves the reaction between PRPP and ATP, which activates the latter to ring cleavage. Carbon atoms from ribose in PRPP form the linear chain and part of the imidazole ring in histidine.[15][16][17] The same is true for the biosynthesis of tryptophan, with the first step being N-alkylation of anthranilic acid catalysed by the enzyme anthranilate phosphoribosyltransferase.[15][18][19]
Increased PRPP
Increased levels of PRPP are characterized by the overproduction and accumulation of uric acid leading to hyperuricemia and hyperuricosuria. It is one of the causes of gout.[20]
Increased levels of PRPP are present in Lesch–Nyhan Syndrome. Decreased levels of hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HGPRT) causes this accumulation, as PRPP is a substrate used by HGPRT during purine salvage.[21]
