Organotantalum chemistry is the chemistry of chemical compounds containing a carbon-to-tantalum chemical bond. A wide variety of compound have been reported, initially with cyclopentadienyl and CO ligands. Oxidation states vary from Ta(V) to Ta(-I).

Classes of organotantalum compounds

Alkyl and aryl complexes
Pentamethyltantalum was reported by Richard Schrock in 1974.[1]
Salts of [Ta(CH3)6]− are prepared by alkylation of TaF5 using methyl lithium:[2]
- TaF5 + 6 LiCH3 → Li[Ta(CH3)6] + 5 LiF
Alkylidene complexes
Tantalum alkylidene complexes arise by treating trialkyltantalum dichloride with alkyl lithium reagents. This reaction initially forms a thermally unstable tetraalkyl-monochloro-tantalum complex, which undergoes α-hydrogen elimination, followed by alkylation of the remaining chloride.[1]
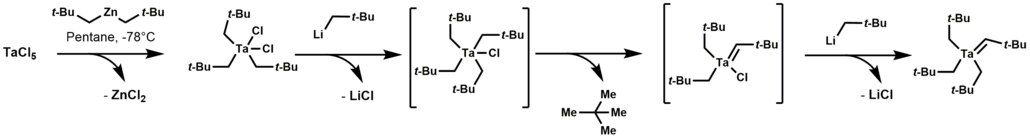
Tantalum alkylidene complexes are nucleophilic.[1] They effect a number of reactions including: olefinations, olefin metathesis, hydroaminoalkylation of olefins, and conjugate allylation of enones.

Ethylene, propylene, and styrene react with tantalum alkylidene complexes to yield olefin metathesis products.[3]
Cyclopentadienyl complexes
Some of the first reported organotantalum complexes were cyclopentadienyl derivatives. These arise from the salt metathesis reactions of sodium cyclopentadienide and tantalum pentachloride. An example of this is the first transition metal trihydride, Cp2TaH3. More soluble and better developed are derivatives of pentamethylcyclopentadiene such as Cp*TaCl4, Cp*2TaCl2, and Cp*2TaH3.[4]

Tantalum carbonyls and isocyanides
Reduction of TaCl5 under an atmosphere of CO gives the salts of [Ta(CO)6]−.[5] These same anions can be obtained by carbonylation of tantalum arene complexes.
A number of tantalum isocyanide complexes are also known.[6]
Tantalum arenes and alkyne complexes
Treatment of tantalum pentachloride with hexamethylbenzene (C6Me6), aluminium, and aluminium trichloride gives [M(η6-C6Me6)AlCl4]2.[7]
Tantalum-alkyne complexes[8] catalyze cyclotrimerizations.[9][10] Some tantalum-alkyne complexes are precursors to allylic alcohols.[11] Tantalacyclopropenes are invoked as intermediates.

Tantalum-amido complexes
Organotantalum compounds are invoked as intermediates in C-alkylation of secondary amines with 1-alkenes using Ta(NMe2)5.[12] The chemistry developed by Maspero was later brought to fruition when Hartwig and Herzon reported the hydroaminoalkylation of olefins to form alkylamines:[13]

The catalytic cycle may proceed by β-hydrogen abstraction of the bisamide, which forms the metallaaziridine. Subsequent olefin insertion, protonolysis of the tantalum-carbon bond, and β-hydrogen abstraction affords the alkylamine product.[14][15][16]

Transmetalation
Organotantalum reagents arise via transmetalation of organotin compounds with tantalum(V) chloride.[17] These organotantalum reagents promote the conjugate allylation of enones. Although the direct allylation of carbonyl groups is prevalent throughout the literature, little has been reported on the conjugate allylation of enones.[18]
Applications
Organotantalum compounds are of academic interest, but few or no commercial applications have been described.