Lithium sulfide is the inorganic compound with the formula Li2S. It crystallizes in the antifluorite motif, described as the salt (Li+)2S2−. It forms a solid yellow-white deliquescent powder. In air, it easily hydrolyses to release hydrogen sulfide (rotten egg odor).[2]
 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Lithium hydrosulfide | |
| Preferred IUPAC name Lithium sulfide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.013 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Li2S | |
| Molar mass | 45.95 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.67 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 938 °C (1,720 °F; 1,211 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,372 °C (2,502 °F; 1,645 K) |
| very soluble, hydrolyses to LiOH and H2S | |
| Solubility | very soluble in ethanol |
| Structure | |
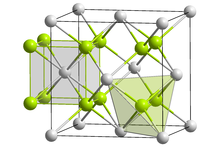
| Antifluorite (cubic), cF12 | |
| Fm3m, No. 225 | |
| Tetrahedral (Li+); cubic (S2−) | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 63 J/mol K |
Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -9.401 kJ/g or -447 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) | 240 mg/kg (oral, rat)[1] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions | Lithium oxide Lithium selenide Lithium telluride Lithium polonide |
Other cations | Sodium sulfide Potassium sulfide Rubidium sulfide Caesium sulfide |
Related compounds | Lithium hydrosulfide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Preparation
Lithium sulfide is prepared by treating lithium with sulfur. This reaction is conveniently conducted in anhydrous ammonia.[3]
- 2 Li + S → Li2S
The THF-soluble triethylborane adduct of lithium sulfide can be generated using superhydride.[4]
Reactions and applications
Lithium sulfide has been considered for use in lithium–sulfur batteries.[5]
References
External links
🔥 Top keywords: Main PageSpecial:SearchPage 3Wikipedia:Featured picturesHouse of the DragonUEFA Euro 2024Bryson DeChambeauJuneteenthInside Out 2Eid al-AdhaCleopatraDeaths in 2024Merrily We Roll Along (musical)Jonathan GroffJude Bellingham.xxx77th Tony AwardsBridgertonGary PlauchéKylian MbappéDaniel RadcliffeUEFA European Championship2024 ICC Men's T20 World CupUnit 731The Boys (TV series)Rory McIlroyN'Golo KantéUEFA Euro 2020YouTubeRomelu LukakuOpinion polling for the 2024 United Kingdom general electionThe Boys season 4Romania national football teamNicola CoughlanStereophonic (play)Gene WilderErin DarkeAntoine GriezmannProject 2025
