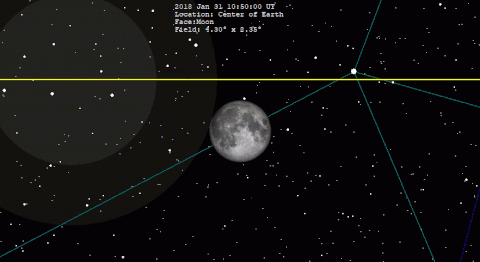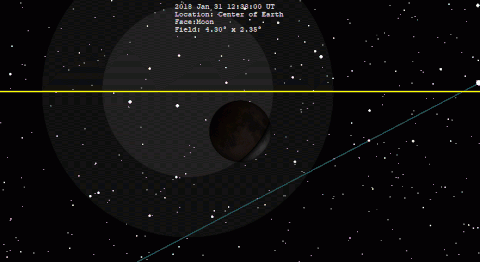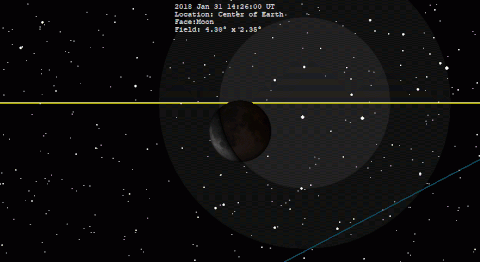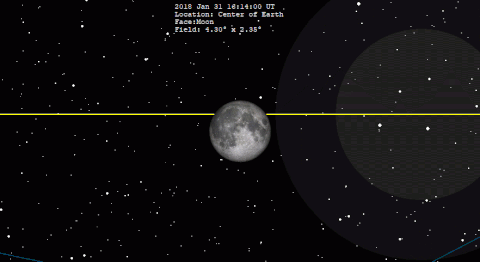
A total lunar eclipse occurred on 31 January 2018. The Moon was near its perigee on 30 January and as such may be described as a "supermoon", when the Moon's distance from the Earth is less than 360,000 km (223,694 miles). The previous supermoon lunar eclipse was in September 2015.[1]
| Total eclipse | |||||||||||||||||
 Totality as viewed from Lomita, California | |||||||||||||||||
| Date | 31 January 2018 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma | −0.3014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Magnitude | 1.3155 | ||||||||||||||||
| Saros cycle | 124 (49 of 74) | ||||||||||||||||
| Totality | 76 minutes, 4 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Partiality | 202 minutes, 44 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| Penumbral | 317 minutes, 12 seconds | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
During the total lunar eclipse of Wednesday, 31 January 2018, the Moon was 360,202 km (only 202 km to be a Super Full Moon) (223,819 mi) from the Earth. A blue moon occurs because there are 2 full moons in the same calendar month, or if there are 4 full moons in the same season (third of four is blue moon). As this supermoon was also a blue moon (the second full moon in a calendar month), it was referred to as a "super blue blood moon"; "blood" refers to the typical red color of the Moon during a total lunar eclipse. The 31 January, 2018 lunar event was called 'Trifecta'.[2] This coincidence last occurred on 30 December 1982 for the eastern hemisphere,[3] and otherwise before that on 31 March 1866.[4][5] The next occurrence will be on 31 January 2037, one metonic cycle (19 years) later.
Background
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes within Earth's umbra (shadow). As the eclipse begins, Earth's shadow first darkens the Moon slightly. Then, the shadow begins to "cover" part of the Moon, turning it a dark red-brown color (typically – the color can vary based on atmospheric conditions). The Moon appears to be reddish because of Rayleigh scattering (the same effect that causes sunsets to appear reddish) and the refraction of that light by Earth's atmosphere into its umbra.[6]
The following simulation shows the approximate appearance of the Moon passing through Earth's shadow. The northern portion of the Moon is closest to the center of the shadow, making it darkest and reddest in appearance.
"Super blue blood moon"
This was a "supermoon", as the Moon was near to its closest distance to earth in its elliptical orbit, making it 7% larger in apparent diameter or 14% larger in area, than an average full moon. The previous supermoon lunar eclipse was the September 2015 lunar eclipse.[1]
The full moon of 31 January 2018 was the second full moon that calendar month (in most time zones), making it, under one definition of the term, a "blue moon".
Additionally referencing the orange or red "blood" colors that occur during a lunar eclipse, media sources described the event as a "super blue blood Moon".[7]
Characteristics
Visibility
The Pacific Ocean was turned toward the Moon at the time of the eclipse. Central and eastern Asia (including most of Siberia), Philippines, Indonesia, New Zealand and most of Australia got a good view of this moon show in the evening sky. For Western Asia, the Indian subcontinent, the Middle East and Eastern Europe, the eclipse was underway as the moon rose.[8]
Along the U.S. West Coast, the total phase began at 4:51 a.m. PST. The further east, the closer the start of the partial phases coincided with moonset. Along the U.S. Atlantic Seaboard, for instance, the Moon had only just begun to enter the darkest part of Earth's shadow, the umbra, at 6:48 a.m. EST when it disappeared from view below the west-northwest horizon. The duration of the total phase was 77 minutes, with the Moon tracking through the southern part of the Earth's shadow. During totality, the Moon's lower limb appeared brighter than the dark upper limb.[8]
  |
 Visibility map |
Timing
| Eclipse | HST | AKST | PST | MST | CST | EST | UTC | MSK | IST | ICT | CST | JST | AEDT | NZDT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zone from UTC | −10 h | −9 h | −8 h | −7 h | −6 h | −5 h | 0 h | +3 h | +5½ h | +7 h | +8 h | +9 h | +11 h | +13 h |
| Penumbral eclipse begins | 00:51 | 01:51 | 02:51 | 03:51 | 04:51 | 05:51 | 10:51 | 13:51 | — | 17:51 | 18:51 | 19:51 | 21:51 | 23:51 |
| Partial eclipse begins | 01:48 | 02:48 | 03:48 | 04:48 | 05:48 | 06:48 | 11:48 | 14:48 | 17:18 | 18:48 | 19:48 | 20:48 | 22:48 | 00:48 |
| Total eclipse begins | 02:52 | 03:52 | 04:52 | 05:52 | 06:52 | — | 12:52 | 15:52 | 18:22 | 19:52 | 20:52 | 21:52 | 23:52 | 01:52 |
| Mid-eclipse | 03:30 | 04:30 | 05:30 | 06:30 | — | — | 13:30 | 16:30 | 19:00 | 20:30 | 21:30 | 22:30 | 00:30 | 02:30 |
| Total eclipse ends | 04:08 | 05:08 | 06:08 | 07:08 | — | — | 14:08 | 17:08 | 19:38 | 21:08 | 22:08 | 23:08 | 01:08 | 03:08 |
| Partial eclipse ends | 05:11 | 06:11 | 07:11 | — | — | — | 15:11 | 18:11 | 20:41 | 22:11 | 23:11 | 00:11 | 02:11 | 04:11 |
| Penumbral eclipse ends | 06:08 | 07:08 | — | — | — | — | 16:08 | 19:08 | 21:38 | 23:08 | 00:08 | 01:08 | 03:08 | 05:08 |
- Example in Aichi Prefecture, Japan:
- Penumbral lunar eclipse 20:23 (JST)
- Partial lunar eclipse 21:13 (JST)
- Partial lunar eclipse 21:43 (JST)
- Total lunar eclipse (blood moon) 21:55 (JST)
Gallery
North America
- Fayetteville, North Carolina, 11:36 UTC
- Partial from Naval Base Point Loma, California
- Melbourne, Florida, 12:00 UTC
- Jacksonville, Florida, 12:10 UTC
- Macon, Georgia, 12:11 UTC
- Tula, Tamaulipas, 12:29 UTC
- Houston, Texas, 12:41 UTC
- Dallas, Texas, 12:51 UTC
- Totality from Southern California, 12:58 UTC
- Denver, Colorado, 12:59 UTC
- Yellowstone National Park, 13:03 UTC
- Placitas, New Mexico, 13:35 UTC
- Redwood City, California, 13:43 UTC
- Novato, California, 14:13 UTC
Asia and Middle East
- Partial from Ilagan, Isabela
- Hiroshima, Japan, 11:43 UTC
- Shinjyuku, Tokyo, 12:52 UTC
- Chiang Mai, Thailand, 12:57 UTC
- Chōfu, Tokyo, 13:22 UTC
- Guangzhou, China, 13:50 UTC
- Kerala, India, 14:03 UTC
- Novosibirsk, Russia, 14:06 UTC
- George Town, Malaysia, 14:16 UTC
- Singapore, 14:32 UTC
- From Kuwait at moonrise, 15:03 UTC
- Nanjing, China, 15:10 UTC
- From Russian Far East
Oceania
- Lake Wendouree, Victoria, 12:40 UTC
- Sydney, Australia, 12:49 UTC
- Chelsea, Victoria, 13:44 UTC
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2018
- A total lunar eclipse on 31 January.
- A partial solar eclipse on 15 February.
- A partial solar eclipse on 13 July.
- A total lunar eclipse on 27 July.
- A partial solar eclipse on 11 August.
The January 2018 lunar eclipse is the first ascending node eclipse of the lunar eclipse series sets from 2016 to 2020. It is also part of Saros cycle 124.
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 2016–2020 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||||
| Saros | Date | Type Viewing | Gamma | Saros | Date Viewing | Type Chart | Gamma | |
| 109 | 2016 Aug 18 | Penumbral | 1.56406 | 114 | 2017 Feb 11 | Penumbral | −1.02548 | |
119 | 2017 Aug 07 | Partial | 0.86690 | 124 | 2018 Jan 31 | Total | −0.30143 | |
129 | 2018 Jul 27 | Total | 0.11681 | 134 | 2019 Jan 21 | Total | 0.36842 | |
139 | 2019 Jul 16 | Partial | −0.64300 | 144 | 2020 Jan 10 | Penumbral | 1.07270 | |
| 149 | 2020 Jul 05 | Penumbral | −1.36387 | |||||
| Last set | 2016 Sep 16 | Last set | 2016 Mar 23 | |||||
| Next set | 2020 Jun 05 | Next set | 2020 Nov 30 | |||||
A similar eclipse occurs on 31 January 2037, one metonic cycle of 19 years in the future.
Half-Saros cycle
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros).[9] This lunar eclipse is related to two annular solar eclipses of Solar Saros 131.
| 26 January 2009 | 6 February 2027 |
|---|---|
 |  |
See also
References
External links

- 2018 Jan 31 chart: Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Hermit eclipse: 2018-01-31