Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP), or noninfectious pneumonia[1] are a class of diffuse lung diseases. These diseases typically affect the pulmonary interstitium, although some also have a component affecting the airways (for instance, cryptogenic organizing pneumonitis). There are seven recognized distinct subtypes of IIP.[2]
| Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Noninfectious pneumonia |
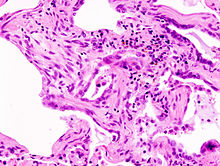 | |
| Micrograph of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). UIP is the most common pattern of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia and usually represents idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. H&E stain. Autopsy specimen. | |
| Specialty | Respirology |
Diagnosis
Classification can be complex,[3] and the combined efforts of clinicians, radiologists, and pathologists can help in the generation of a more specific diagnosis.[4][5]
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia can be subclassified based on histologic appearance into the following patterns:[6][7]
| Histology | Clinical Correlates |
|---|---|
| Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP) | DIP |
| Diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) | ARDS, AIP, TRALI |
| Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) | NSIP |
| Respiratory bronchiolitis | RB-ILD |
| Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) | CVD, IPF, drug toxicity, pneumoconiosis |
| Organizing pneumonia | Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia |
| Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP) | LIP |
Usual interstitial pneumonia is the most common type.[8]
Development
Table 1: Development of the (histologic) idiopathic interstitial pneumonia classification
| Leibow et al. (1969) | Katzenstein (1998)[9] | ATS/ERS (2002)[7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UIP | UIP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UIP | DAD | DAD | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NSIP | NSIP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DIP | DIP/RB | DIP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RB | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BIP | OP | OP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LIP | (LPD) | LIP | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GIP | (HMF) | (HMF) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
UIP=usual interstitial pneumonia; DAD=diffuse alveolar damage; NSIP=non-specific interstitial pneumonia; DIP=desquamative interstitial pneumonia; RB=respiratory bronchiolitis; BIP=bronchiolitis obliterans interstitial pneumonia; OP=organizing pneumonia; LIP=lymphoid interstitial pneumonia; LPD=lymphoproliferative disease (not considered a diffuse lung disease); GIP=giant cell interstitial pneumonia; HMF=heavy metal fibrosis, no longer grouped with diffuse lung disease
Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia was originally included in this category, then excluded, then included again.[10]