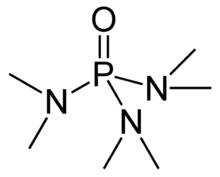
Hexamethylphosphoramide, often abbreviated HMPA, is a phosphoramide (an amide of phosphoric acid) with the formula [(CH3)2N]3PO. This colorless liquid is a useful reagent in organic synthesis.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name Hexamethylphosphoric triamide[3] | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| 1099903 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.595 |
| EC Number |
|
| 3259 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2810 3082 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H18N3OP | |
| Molar mass | 179.20 g/mol |
| Appearance | clear, colorless liquid[4] |
| Odor | aromatic, mild, amine-like[4] |
| Density | 1.03 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 7.20 °C (44.96 °F; 280.35 K) |
| Boiling point | 232.5 °C (450.5 °F; 505.6 K) CRC[5] |
| miscible[4] | |
| Vapor pressure | 0.03 mmHg (4.0 Pa) at 20 °C[4] |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards | Suspected Carcinogen[4] |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Danger | |
| H340, H350 | |
| P201, P202, P281, P308+P313, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 104.4 °C (219.9 °F; 377.5 K) |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible) | none[4] |
REL (Recommended) | Ca[4] |
IDLH (Immediate danger) | Ca [N.D.][4] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Oxford MSDS |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Structure and reactivity
HMPA is the oxide tris(dimethylamino)phosphine, P(NMe2)3. Like other phosphine oxides (such as triphenylphosphine oxide), the molecule has a tetrahedral core and a P=O bond that is highly polarized, with significant negative charge residing on the oxygen atom.
Compounds containing a nitrogen–phosphorus bond typically are degraded by hydrochloric acid to form a protonated amine and phosphate.
It dissolves alkali metal salts[6] and alkali metals, forming blue solutions which are stable for a few hours. Solvated electrons are present in these blue solutions.[7]
Applications
HMPA is a specialty solvent for polymers, gases, and organometallic compounds. It improves the selectivity of lithiation reactions by breaking up the oligomers of lithium bases such as butyllithium. Because HMPA selectively solvates cations, it accelerates otherwise slow SN2 reactions by generating more bare anions. The basic nitrogen centers in HMPA coordinate strongly to Li+.[8]
HMPA is a ligand in the useful reagents based on molybdenum peroxide complexes, for example, MoO(O2)2(HMPA)(H2O) is used as an oxidant in organic synthesis.[9]
Alternative reagents
Dimethyl sulfoxide can often be used in place of HMPA as a cosolvent. Both are strong hydrogen bond acceptors, and their oxygen atoms bind metal cations. Other alternatives to HMPA include the N,N′-tetraalkylureas DMPU (dimethylpropyleneurea)[10][11] or DMI (1,3-dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone).[12] Tripyrrolidinophosphoric acid triamide (TPPA) has been reported to be a good substitute reagent for HMPA in reductions with samarium diiodide[13] and as a Lewis base additive to many reactions involving samarium ketyls.[14]
Toxicity
HMPA is only mildly toxic but has been shown to cause cancer in rats.[8] HMPA can be degraded by the action of hydrochloric acid.
References
External links
- "Hexamethylphosphoramide CAS No. 680-31-9" (PDF). Report on Carcinogens (12th ed.). National Toxicology Program, Department of Health and Human Services. 2011.
- "Hexamethyl phosphoramide". NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Department of Health and Human Services. 2011.
- Merck Index. Vol. 4761 (12th ed.).