Camostat is a serine protease inhibitor. Serine protease enzymes have a variety of functions in the body, and so camostat has a diverse range of uses. Camostat is approved in Japan for the treatment of chronic pancreatitis and postoperative reflux esophagitis.[1][2] The oral proteolytic enzyme inhibitor has been on the market since 1985 under the trade name Foipan Tablets. The manufacturer is Ono Pharmaceutical. The drug is used in the treatment of some forms of cancer and is also effective against some viral infections, as well as inhibiting fibrosis in liver or kidney disease or pancreatitis.[3][4][5][6][7]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Foipan |
| Other names | FOY-305 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
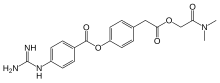
| Formula | C20H22N4O5 |
| Molar mass | 398.419 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Pharmacology
It is an inhibitor of the enzyme transmembrane protease, serine 2 (TMPRSS2).For chronic pancreatitis camostat's typical dose is 600 mg daily, for postoperative reflux esophagitis 300 mg are taken. The daily dose is split in 3 doses and taken after each meal.[1][8]
Side effects
As side effects allergic reactions including anaphylaxis, hypersensitivity, hyperkalemia, platelet and leukocyte depletion, liver dysfunction, jaundice have been reported.[9]
COVID-19

Inhibition of TMPRSS2 partially blocked infection by SARS-CoV and Human coronavirus NL63 in HeLa cell cultures.[10]Another in vitro study showed that camostat significantly reduces the infection of Calu-3 lung cells by SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19.[11][12] It is currently in many Phase 1 and Phase 2 clinical trials.[13][14]
Camostat decreased CRP levels better compared to Lopinavir/Ritonavir in a small study of mild COVID-19 patients.[15] Camostat decreased COVID-19 severity, improved inflammatory markers and oxygenation compared to hydroxychloroquine treated patients.[16][12]
A study of 205 COVID-19 patients treated with Camostat, carried out at Aarhus University Hospital in Denmark and concluding in April 2021, showed no noticeable effects of Camostat on duration of hospitalisation or severity of the cases, but noted that higher doses (the study used 600 mg Camostat daily dosage) might still have a possible effect.[17]
On July 1, 2021, the AIDS Clinical Trials Group announced that the Camostat group on the "ACTIV-2 Outpatient Monoclonal Antibodies and Other Therapies Trial" would not be moving forward to Phase 3. The trial demonstrated no safety concerns but also no changes in viral shedding or symptom improvement.[18]
References
External links
- Kunze H, Bohn E (May 1983). "Effects of the serine protease inhibitors FOY and FOY 305 on phospholipase A1 (EC 3.1.1.32) activity in rat - liver lysosomes". Pharmacological Research Communications. 15 (5): 451–459. doi:10.1016/S0031-6989(83)80065-4. PMID 6412250.
- Göke B, Stöckmann F, Müller R, Lankisch PG, Creutzfeldt W (1984). "Effect of a specific serine protease inhibitor on the rat pancreas: systemic administration of camostate and exocrine pancreatic secretion". Digestion. 30 (3): 171–178. doi:10.1159/000199102. PMID 6209186.
