Bifonazole (trade name Canespor among others[1]) is an imidazole antifungal drug used in form of ointments.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Canespor, many others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.056.651 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
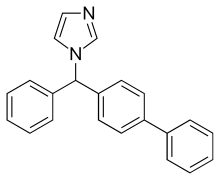
| Formula | C22H18N2 |
| Molar mass | 310.400 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
| |
It was patented in 1974 and approved for medical use in 1983.[2] There are also combinations with carbamide for the treatment of onychomycosis.
Adverse effects
The most common side effect is a burning sensation at the application site. Other reactions, such as itching, eczema or skin dryness, are rare.[3]Bifonazole is a potent aromatase inhibitor in vitro.[4][5]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Bifonazole has a dual mode of action. It inhibits fungal ergosterol biosynthesis at two points, via transformation of 24-methylendihydrolanosterol to desmethylsterol, together with inhibition of HMG-CoA. This enables fungicidal properties against dermatophytes and distinguishes bifonazole from other antifungal drugs.[3][6]
Pharmacokinetics
Six hours after application, bifonazole concentrations range from 1000 μg/cm3 in the stratum corneum to 5 μg/cm3 in the papillary dermis.[3]
Synthesis
Friedel-Crafts acylation between biphenyl (1) and benzoyl chloride (2) gives 4-phenylbenzophenone (3). Reduction with sodium borohydride gives the alcohol (4). Halogenation by thionyl chloride gives (5). Amination with imidazole (6) completes the synthesis of bifonazole.[7][8][9]
