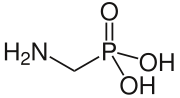
Aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA) is a weak organic acid with a phosphonic acid group.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name (Aminomethyl)phosphonic acid | |
| Other names Aminomethanephosphonic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| Abbreviations | AMPA; AMeP |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.152.014 |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH6NO3P | |
| Molar mass | 111.037 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Melting point | 338 to 344 °C (640 to 651 °F; 611 to 617 K) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.4 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Application
AMPA apparently can be used as biocide and pesticide.[1] AMPA is also used in research to assess the exposure of glyphosate.[2]

Environmental fate
AMPA is one of the primary degradation products of the herbicide glyphosate[4] and the related chemical glyphosat-trimesium.[1]
AMPA has the potential to be broken down further by manganese oxide in laboratory conditions, however in soil manganese oxide is usually only present in trace amounts.[5] Microbial degradation of AMPA is the more likely degradation pathway, where it degrades into phosphoric acid[6][7] and ultimately to carbon dioxide and inorganic phosphate.[8]
Toxicity
AMPA has toxicity which is comparable to that of glyphosate and it is therefore considered to be of similar toxicological concern (harmful in greater than 0.5 parts per million) as glyphosate itself.[9]